Praca z ramkami graficznymi
- Linkownia
- Zrobione w Scribusie
- Gazety i czasopisma
- Polska lokalizacja Scribusa
- Darmowe polskie fonty
- Słowniczek pojęć z DTP
- Pierwsze kroki ze Scribusem
- Praca z ramkami tekstowymi
- Praca z ramkami graficznymi
- Praca ze stronami wzorcowymi
- Praca w Edytorze artykułów
- Tekst na krzywej
- Scribus w Ubuntu Linux
- Klik i Scribus działa
- Instalacja za pomocą Cmake
- Tworzenie spisu treści
- Formularze PDF
- Kolory dodatkowe
- Obrazek ze ścieżką odcięcia
- Instalacja profili ICC
- Dodawanie fontów
- Import grafik EPS
- Zawieszone spójniki
- Twój pierwszy artykuł
- Tworzenie hiperłączy
- Zarządzanie kolorami
- Skąd pobrać Scribusa?
- Podgląd wydruku nie działa
- Scribus dla MacOSX?
- Dodawanie fontów
- Scribus po polsku
- Type 1 i ligatury
- Automatyczne numery stron
- Interlinia w Scribusie
- Pierwsze kroki z DTP
- Skalowanie obrazka w ramce
- Export do PDF/X-3
- Ligatury i cyfry nautyczne?
- Pomoc w rozwoju Scribusa
- Przykładowe dokumenty
- Zgłaszanie błędów
- Słowniki dzielenia na sylaby
Tłumaczenie w toku!
This article is intended to be a compilation of operations pertaining to image frames. Much of how Scribus is used is intuitive, yet you may find there are features you have missed or more straightforward ways here.
Tworzenie
Możesz utworzyć ramkę graficzną poprzez:
- kliknięcie ikony Wstaw ramkę graficzną na pasku narzędzi
- wybranie pozycji Wstaw > Ramka graficzna z menu
- skrót klawiszowy I lub Alt+W, I
Pozwoli to na umiejscowienie i wybranie rozmiaru ramki za pomocą myszy. Aby tego dokonać przyciśnij lewy klawisz myszy, a następnie przeciągnij kursor po przekątnej strony. Przyciśnięcie klawisza myszy wyznacza jeden róg ramki, a puszczenie go wyznaczy róg znajdujący się na końcu przekątnej. Najbardziej typowym sposobem jest zaczęcie w lewym górnym rogu, jednakże można zacząć w dowolnym z nich.
Usuwanie
Usuń wybraną ramkę przyciskając klawisz Delete lub Ctrl+X.
Menu kontekstowe
Klikając prawym klawiszem myszki uzyskasz dostęp do menu kontekstowego, które zawiera najczęściej wykonywane operacje na ramkach, z których jedną z ważniejszych jest możliwość zamiany ramki graficznej na inny typ ramki.
Pozycja i rozmiar
W tym punkcie zauważysz, że okno Właściwości jest niezastąpionym elementem podczas pracy ze Scribusem. Jeśli nie widzisz jeszcze okna dialogowego Właściwości, możesz je otworzyć poprzez skorzystanie z menu Okna > Właściwości. Zakładka XYZ okna Właściwości pokazuje bardzo dokładne informacje o pozycji punktów X i Y lewego górnego rogu wybranej ramki, której obrys zaznaczony jest czerwoną, przerywaną linią. Ramka jest automatycznie wybierana w chwili jej utworzenia. Możesz odznaczyć ramkę klikając na obszar poza jej granicami, a zaznaczyć ponownie klikając w jej wnętrzu. Ramka musi zostać zaznaczona, aby mogła być modyfikowana lub przestawiana.
Ładowanie obrazków do ramki graficznej
| Ramka, którą utworzysz, będzie początkowo pusta oprócz litery X umieszczonej wewnątrz, oznaczającej fakt iż nie załadowano żadnego obrazku.
Możesz importować pliki w formacie TIFF, JPEG, PNG, GIF, XPM oraz EPS. Istnieje też możliwość zaimportowania dokumentu PDF, jednakże na chwilę obecną tylko pierwsza strona zostanie załadowana (patrz niżej, by znaleźć sposób obejścia tego problemu). Załaduj obrazek za pomocą menu kontekstowego (poprzez kliknięcie prawym klawiszem myszy w obrębie ramki) > Pobierz obrazek, za pomocą menu Plik > Importuj > Pobierz obrazek... (lub odpowiednich skrótów klawiszowych). Domyślnie obrazek zostanie załadowany z jego domyślnym rozmiarem oraz jego lewy górny róg będzie lewym górnym rogiem ramki. Prawdopodobnie wystarczy, że będzie potrzebna tylko zmiana rozmiaru ramki, by dopasować obrazek, jednakże najczęściej będzie wymagana również zmiana skali obrazka. Jeśli znasz docelowy rozmiar ramki, zapoznaj się z radami w następnym dziale, po czym przejdź do Właściwości: Zakładka Obrazek. |
Co z plikami SVG?
Pliki SVG są otwartym formatem graficznym i potrafi być wręcz idealny dla DTP. Obrazki SVG nie używają ramek, lecz mogą być przesuwane i skalowane, a także częściowo edytowane. Niektóre cechy formatu nie są jeszcze obsługiwane przez Scribusa, więc w tej chwili dla pewnych obrazków należy skorzystać z funkcji eksportu do jednego z formatów w ramce obok aplikacji typu Inkscape lub Sodipodi, a następnie umieścić je w zwykłej ramce graficznej Jeśli wybierzesz to rozwiązanie, najlepiej ustaw znacznie większą rozdzielczość (DPI) niż domyślną, by zredukować efekt pikselizacji w finalnym dokumencie. |
| Importowanie wielostronicowych dokumentów PDF
Obecnie jest to możliwe tylko z użyciem zewnętrznego oprogramowania, takiego jak Adobe Acrobat. Istnieje też otwarty program o nazwie pdftk, który potrafi rozbić wielostronicowy dokument PDF na kilka dokumentów zawierających tylko jedną stronę. Zauważ również, iż Scribus potrafi eksportować PDF-y jako pojedyncze strony – znajdziesz tą opcję podczas eksportu dokumentu. |
Właściwości: Zakładka XYZ - Zmiana rozmiaru/pozycji
Za pomocą myszy:
- Kliknij we wnętrzu ramki i przeciągnij na wybraną pozycję. Ramki mogą być umieszczane również poza stroną lub przesuwane z jednej strony na drugą (w zależności od wersji Scribusa).
- Kliknij i przeciągnij dowolny z czerwonych prostokącików umieszczonych na rogach i bokach ramki, by zmienić jej rozmiar.
Za pomocą okna Właściwości:
Istnieją 3 sposoby zmiany poszczególnych ustawień:
- edycja za pomocą klawiatury
- klikając na strzałkach w górę lub w dół umieszczonych na prawo od każdej wartości. Naciskając klawisze kursorów na klawiaturze uzyskasz ten sam efekt.
- używając rolki myszy – zazwyczaj ustawienie kursora nad polem w zupełności wystarcza, jeśli nie, kliknij w nie najpierw
Zauważ, że dla drugiego i trzeciego sposobu, równoczesne przytrzymanie klawiszy Ctrl, Shift lub Ctrl+Shift (działa również dla klawiszy kursorów) zmieni również miejsce po przecinku, które będzie edytowane. Poza tym w oknie Właściwości pola wysokości i szerokości są domyślnie ze sobą połączone, lecz wystarczy kliknięcie na ikonę łańcucha, by je rozłączyć.
Dodatkowe informacje
- Wybranie z menu pozycji Strona > Wyrównaj do siatki uaktywni przyciąganie ramek do linii siatki umieszczonych na stronie. Z kolei pozycja menu Widok > Wyświetlaj siatkę przełącza wyświetlanie jej na ekranie. (Siatka nie zostanie nigdy wydrukowana, ani nie staje się częścią dokumentu PDF.) Aby ustawić odstęp między liniami siatki, skorzystaj z ustawień zawartych w menu Plik > Konfiguracja > Linie pomocnicze;
- Wybranie z menu pozycji Strona > Wyrównaj do linii pomocniczych uaktywni przyciąganie ramek do linii pomocnyczych na stronie. Z kolei pozycja menu Widok > Wyświetlaj linie pomocnicze przełącza wyświetlanie ich na stronie. (Podobnie jak w przypadku siatki, linie pomocnicze nie zostaną nigdy wydrukowane, ani nie staną się częścią dokumentu PDF.) Jeżeli zechcesz zmienić lub dodać linie pomocnicze, udaj się do menu Strona > Zarządzaj liniami pomocniczymi lub do Plik > Konfiguracja > Linie pomocnicze.
Properties: Image Tab
If your frame is already the correct size, click Scale to Frame Size. Subsequent adjustments in frame size will adjust scaling to maintain scaling to the frame size. Clicking back to Free Scaling will allow you to crop edges, reposition, or change scaling.
Scaling, Repositioning -- the Image
See Resizing, Repositioning above for instructions on moving and resizing the frame -- Properties: XYZ Tab.
| With the mouse on the frame: | With the Properties window: |
|---|---|
|
Just as in the XYZ tab, there are three ways to change the individual settings --
And again note that for 2 and 3, holding down Ctrl, Shift, or Ctrl+Shift (works with up and down arrow keys also) will alter which decimal place is affected. In addition, when using the Properties, X-Scale, Y-Scale, and X-DPI, Y-DPI are by default linked, but you need only click the chain icon to the right to unlink them. |
X-Pos, Y-Pos: These refer to the offset of the image inside the frame. Negative values will expose the background color of the frame.
X-Scale, Y-Scale, Actual X-DPI, Actual Y-DPI: Default linked, click the chain to unlink. Obviously, scaling and DPI are inversely related, but for high-quality printed output, knowing the end-product DPI is essential to avoid poor quality results. If your end-product will be a PDF for the web or for a presentation, a lower DPI may suffice. See this page at the Scribus website for more details.
Some Additional Info:
The Context Menu (right-click in frame) > Info will give some basic information about your image -- file source, original and final scaling. The menu item Extras > Manage Pictures may also be of help.
Rotation
With the mouse:
Click the Rotate Item icon on the toolbar (keyboard: R), then click inside the frame and drag-rotate to desired angle.
With the Properties window: XYZ Tab
Just like resizing and repositioning, you have the same three ways to change the rotation digitally. There is also an icon just below (looks something like one of a pair of dice) to alter the point around which rotation takes place -- center or one of the four corners.
Copying Frames and Similar Operations
There are several different ways to copy or move frames.
- You should be familiar with Copy and Paste (keyboard: Ctrl+C, Ctrl+V) and Cut and Paste (keyboard: Ctrl+X, Ctrl+V) -- also accessible from Edit on the menu, and from the Context Menu (right-click in frame). To paste to another page, move to that page, click on it, then paste -- the frame will have the same coordinates as on the original page.
- There is also Duplicate (keyboard: Ctrl+Alt+Shift+D) Item > Duplicate. This makes a copy which is slightly offset from the original, and on a layer above it.
- There is Multiple Duplicate, Item > Multiple Duplicate, which brings up a requestor to automatically create as many copies as you wish, with a sequential adjustable offset. You can also use this for a single duplication when you want to set the offset. Note that once you set the offset here, Item > Duplicate will use this same offset.
- Finally, there is the Scrapbook, Item > Send to Scrapbook or from Context Menu (right-click in frame). This will make a named copy of the selected frame and its contents to the Scrapbook. To retrieve a saved item from Scrapbook, select from the menu Windows > Scrapbook, to bring up a requestor to paste an item to a page. Also note that you can save your entire Scrapbook to a file, which can then be loaded and used in another document.
Experimentation will show you that frames can even be outside the document boundaries and still be copied, duplicated and manipulated in various ways. They will even be saved with the document in these locations. If you try to generate a PDF, you will receive error messages about objects not being on the page; if ignored, the PDF will not have these objects. Furthermore, especially in a large multipage document, you may lose track of these off-document objects.
Poziomy i warstwy
Frames in general, not just image frames, represent a two-dimensional space that you manipulate and move around your workspace, much like a small note you can attach and detach. Like small physical notes, they are laid down, one by one, on the page, new ones on a layer over the previous ones. The small box labeled Level in the XYZ tab of Properties allows you to move the selected frame up or down layers; the arrows with bars will move all the way to the top or bottom. Since the background of your frame may be opaque or transparent, the level the frame is at will affect how much of the frame can be visible in relationship to other overlapping or underlying frames.
XYZ Tab: The Rest
The remaining buttons in the XYZ tab do the following:
- Flip the selected frame horizontally or vertically
- Lock a frame in place. Everything about your frame is locked -- size, position, contents. Copying and pasting a locked frame may produce unexpected results.
- Lock the size of the frame only. Note that the editing tabs disappear from the corners and sides.
- Enable/disable printing of the frame. Why? You may want to have a frame on the page that's a message to yourself or someone else, yet not be part of the printed finished work. Or the frame may just be a space-saver for some other purpose.
Properties: Shape Tab
Click the Shape tab in Properties. Near the top is a button with a square in the center. If you click that button, you may quickly switch to one of a group of set shapes from your original rectangle. In addition, if you click Edit Shape..., you now have full vector-editing control of your shape.
Another angle on shapes and image frames:
You may also use the Polygon tool on the toolbar (use will be described in detail in another section) to create a regular polygon, which may then be converted using the Context Menu (right-click in the polygon) to Convert To > Image Frame.
Round Corners
Causes an adjustable degree of rounding of the Image Frame corners. Also note the effect of negative values.
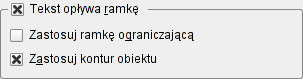
Text Flows Around Frame
| Use this to determine what happens with text underneath the selected frame. Remember Levels & Layers? When you create an image frame, the Bounding Box (of the image) and the Contour Line are the same size and position. But click on Edit Shape... and you can change this Contour Line's size, position, and shape as desired -- check the Edit Contour Line box in the Edit Shape requester. |
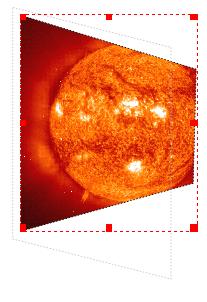
Here is an example: | |
| Here we see that the shape of the image, the Bounding Box (dotted red line), and Contour Line (faint grey dotted line) can occupy separate spaces. The Bounding Box will always have a rectangular shape. |
Properties: Line Tab
The Line of an Image Frame refers to the border of the frame. The first thing to be aware of is that the default setting for Line Color is None, so regardless of the settings in the Line Tab, nothing will show until the Line Color is set.
Otherwise, the various settings for Line are straightforward. If a setting is greyed-out, it does not apply to frames.
Properties: Color Tab
As noted above, the Line Color refers to the border of the frame, with the default being None.
Fill Color means background color of the frame. None for a Fill Color means that the background is transparent.
Shade refers to saturation of the color, so that 0% should represent a neutral grey scale color. Opacity refers to the relative opacity/transparency, with 100% being totally opaque, 0% totally transparent. It is worth noting at this point that some PDF versions and some PDF viewers do not support transparency.
Overprinting versions 1.3.4 and above
Knockout versus Overprinting are described here.
Please note that you are not limited to colors you see displayed in the Color Tab, nor are you compelled to have all these choices. See the Menu item Edit > Colors to add, edit, or remove colors. Removing colors can simplify the use of Scribus, and does reduce saved file size.